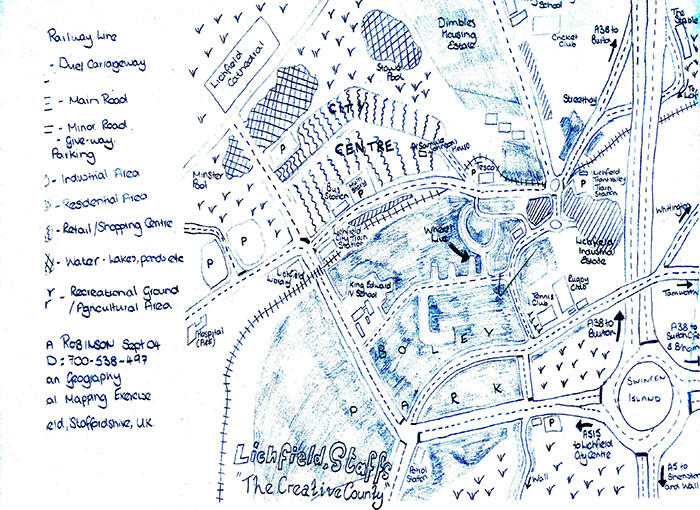
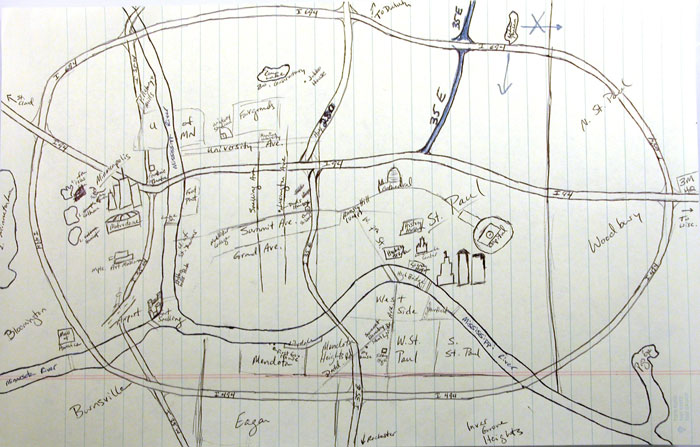
Cognitive Mapping
Cognitive mapping shows users' thoughts of a particular problem space in a visible way.
01 Definition
Cognitive mapping is a visualization of how people make sense of a particular problem space. It is most effective when used to structure complex problems and to inform decision making.
---- Universal Methods of Design p.30
A cognitive map (also: mental map or mental model) is a type of mental representation which serves an individual to acquire, code, store, recall, and decode information about the relative locations and attributes of phenomena in their everyday or metaphorical spatial environment.
---- Wikipedia
02 Natures
- Notes
- How: ask participants to map an existing or virtual space and show how they navigate it (spatial knowledge vs. spatial ability)
- Why: A useful way to discover the significant elements, pathways, and other spatial behavior associated with a real or virtual environment.
- Example: IDEO asked bike messengers in NYC to indicate where water oases are located and how they reach them
03 Examples
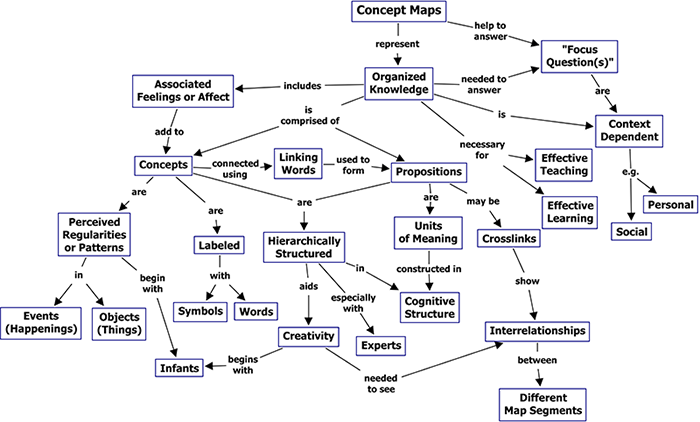
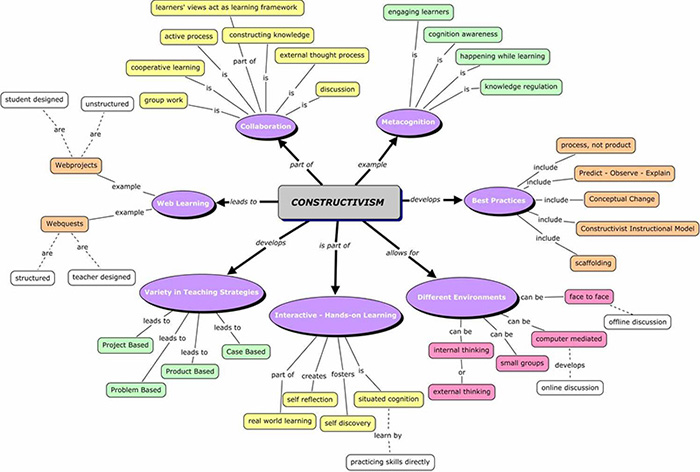
Concept Mapping
Concept mapping is a visual diagram to present the map of user's concepts and the relation between these concepts. By using concept mapping, researchers could learn about the structure of thinking.
01 Definition
Concept mapping is a visual framework that allows designers to absorb new concepts into an existing understanding of a domain so that new meaning can be made.
---- Universal Methods of Design p.38
A concept map is a diagram that depicts suggested relationships between concepts. It is a graphical tool that designers, engineers, technical writers, and others use to organize and structure knowledge. A concept map typically represents ideas and information as boxes or circles, which it connects with labeled arrows in a downward-branching hierarchical structure. The relationship between concepts can be articulated in linking phrases such as causes, requires, or contributes to.
---- Wikipedia
02 Natures
- Notes
- For genealogy analysis: Collect family documents and stories of each artifact; Begin analysis with the present and work backward in time; Use historical records to demonstrate kinship between artifacts.
- For landscape analysis: Identify and classify the possession types, and artifact attributions within a landscape of personal possessions; Analyze the landscape ecology of each objects/artifact/possession; Identify a connected network of diverse relationships distributed across the landscape of possessions.
- Suited Context
- The patterns which are detected in landscape analysis can be used to assess the relations among personal possessions, and to review his/her personalities.
03 Examples
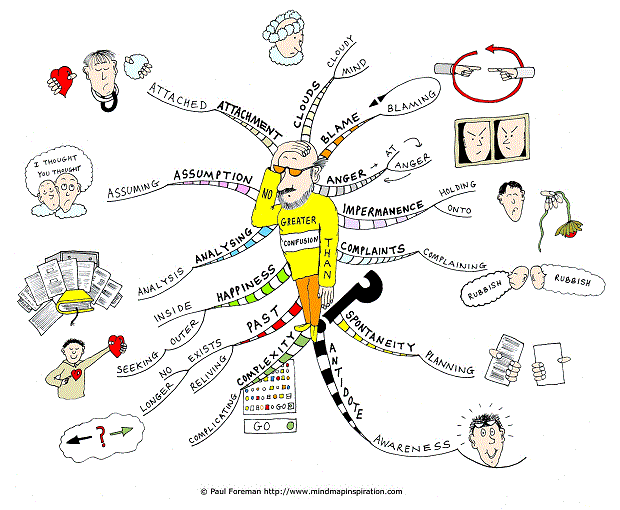
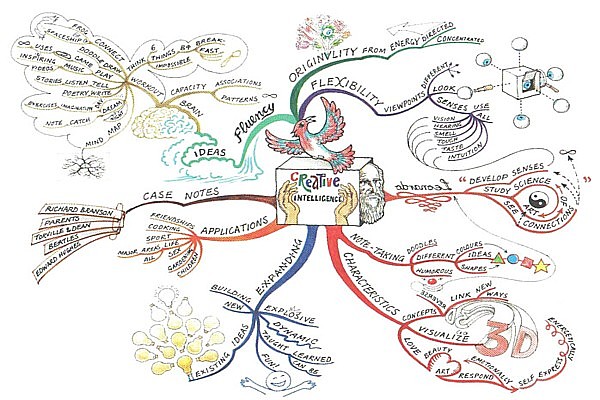
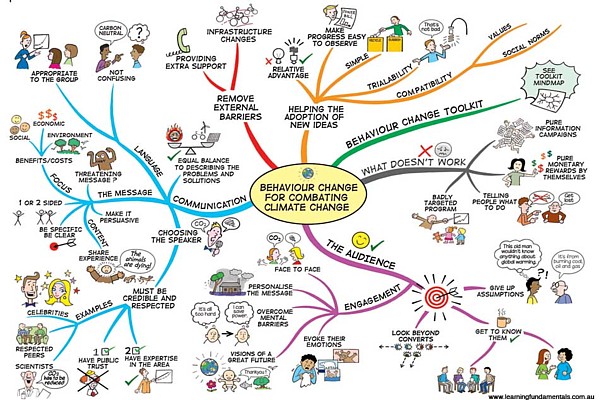
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is the method that online categorized information around specific word and develop information to branches. It could help organizing a problem space systematicly.
01 Definition
When a topic or a problem has many moving parts, mind mapping provides a method of visually organizing a problem space in order to better understand it.
---- Universal Methods of Design p.118
A mind map is a diagram used to visually outline information. A mind map is often created around a single word or text, placed in the center, to which associated ideas, words and concepts are added. Major categories radiate from a central node, and lesser categories are sub-branches of larger branches.
---- Wikipedia
02 Natures
- Notes
- A tool that enables designers to develop an understanding of and generate ideas about the problem space, and highlight areas for further exploration.
- It provides a foundation for designers to create guideline for the project’s user research and/or market focus.
- What to do: Create a matrix to visually and hierarchically map out various areas related to the problem space; There are software available for mind mapping, but in this exercise, you will do it by hand to get a feel of it.
- Suited Context
- The patterns which are detected in landscape analysis can be used to assess the relations among personal possessions, and to review his/her personalities.
03 Examples
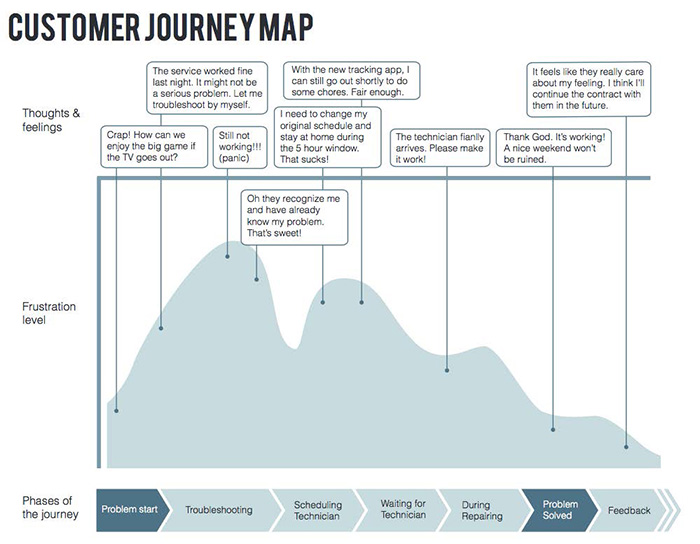
Customer Journey Map
Researchers use Customer Journey Map to record user's feeling and thoughts, according to phrase of journal. They also do observation on user's emotion level at different touch points.
01 Definition
A customer journey map is a tool that fits into the broader context of your customer experience strategy; it requires significant customer insight-driven inputs and internal buy-in to be effective.
---- Customer Journey Mapping: 10 Tips For Beginners
02 Natures
- Notes
- A tool commonly used in service design.
- An “oriented graph that describes the journey of a user by representing different touchpoints (defined as the “interface of a service”) that characterize her interaction with the service.
- Benefits: It highlights the “gaps, pain points, and opportunities of the experience, both from the perspective of the user and the provider.”
03 Examples
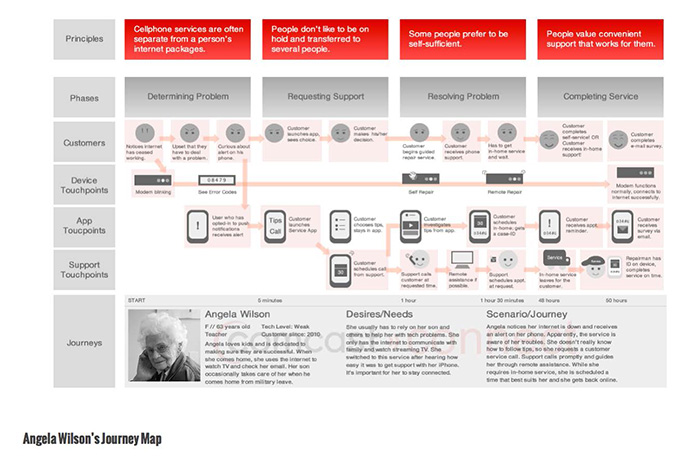
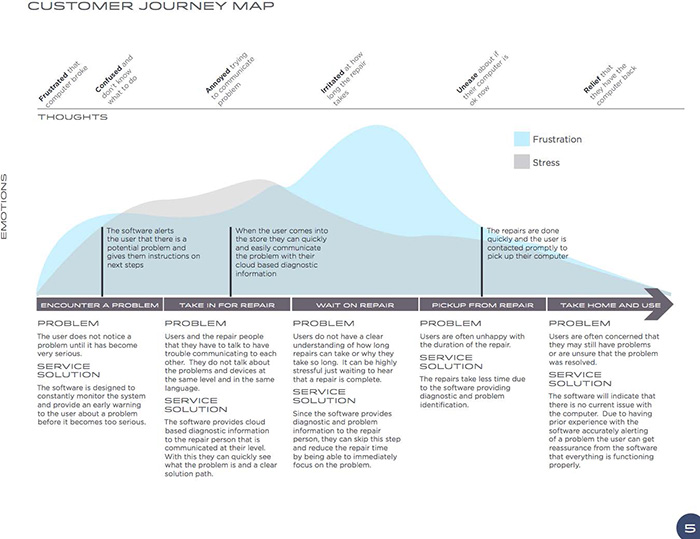
Gengsu Tu |
Copyright © 2014 by Gengsu Tu. All rights reserved.